Microvascular complication!!!
This category of
complication involves the disease of small blood vessels. Commonly, it involves
retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy.
1) Retinopathy (eye damage)
How does diabetes cause
eye damage???
Excessive sugar can damage the tiny blood vessels that nourish the
retina (part of eye). It may severe block the blood vessels. If there are many
blood vessels being blocked, there will be lack of blood supply to the retina.
This can result in vision loss or blindness.
Retinopathy can be divided into 4
stages:
The examples of serious vision conditions are
cataracts (clouding of the lens of the eye) and glaucoma (damaged optic nerve).
Comparison of normal
eye (right) and eye with contract (left)
Screening
·
Individuals aged
10 years or older with type 1 diabetes should have an initial dilated and
comprehensive eye examination by an ophthalmologist or optometrist within 5
years after the beginning of type 1 diabetes.
·
Eye examination
should be taken after the diagnosis for patient with type 2 diabetes.
·
Repeat annually
the examinations for type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients. Less-frequent exams
(every 2–3 years) may be considered for diabetic patients with healthy eyes however
more frequent examinations will be required if retinopathy is progressing.
·
Women who have
diabetes previously and either plan to get pregnancy or have become pregnant
should have a comprehensive eye examination. Counseling about the risk of
development and/or progression of diabetic retinopathy should be given. Eye
examination is encouraged during the first trimester with close follow up throughout
pregnancy and 1yearafterpostpartum.
Treatment
- Diabetic patient with eye complication should refer to an ophthalmologist who is knowledgeable and experienced in the management and treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
- Early retinopathy (non-proliferative) of diabetic patients may not need treatment. However, they should be closely followed by an eye doctor who is trained to treat diabetic eye diseases.
- Treatment is usually needed for severe retinopathy as well as the developing macular edema (swelling of macula results from leakage and accumulation of fluid).
- Medical retinopathy treatment such as surgical or laser treatments is depending on the problem of the retina.
Table shows types of treatment for retinopathy patient.
2) Nephropathy (damage of kidney)
How does diabetes cause kidney problem?
Kidney has millions of tiny blood vessels
(capillaries) with small holes which are involved in the filtration of waste
products. The waste product is the unwanted or useless substances produced as a
result of a process occur in the human body. However, the useful substances
such as proteins and red blood cells are too big to pass through the blood
vessels and supposed to be stay in the blood.
Patients with diabetes can damage the function of
kidney. The high blood sugar level cause the kidney to filter too much blood
thus increases the burden of the kidney. After a long time, the useful proteins
start to leak out and lost in the urine. Albuminuria is diagnosed.
Kidney
damaged is distributed into 3 categories
Symptoms of patients with kidney
problem:
·
Insomnia
·
Loss of appetite
·
Discomfort
feeling of stomach
·
Weakness
·
Hard to
concentrate
Screening
- Assess urine albumin secretion (UAE) annually in type 1 diabetic patients with duration of ≥ 5 years while assess UAE in type 2 diabetes at starting diagnosis.
- Measure the serum creatinine at least annually in all adults with diabetes. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and the stage level of chronic kidney disease can be estimated based on the measurement of serum creatinine, if present.
Criteria of screening test of albuminuria
Treatment
- ACE inhibitor and ARBs should be used to slow down the progression of kidney disease. It lowers theblood pressure by monitoring the serum creatinine and potassium levels of patients.
- Reduction of protein intake to 0.8-1.0 g/kg/day body weight in individuals with diabetes and the earlier stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
- Reduction of protein intake to 0.8 g/kg/day body weight in individuals with later stages of CKD.
- Monitor the serum creatinine and potassium level if ACE inhibitors, ARBs or diuretics are used as there may be increased creatinine and potassium level.
- Evaluate and manage potential complications of CKD if the estimated GFR is < 60 ml.min/1.73 m2.
- Dialysis or a kidney transplant is required for kidney failure or irreversible ESRD.
What may you feel if you are having kidney
failure?
- Swelling in the feet and ankles
- Itching
- Fatigue
- Pale skin colour
3) Neuropathy (damage of nerves)
Excessive sugar
can damage the wall of tiny blood vessels that nourish the nerves, especially
in the legs. It causes slight
prickling sensation (tingling),
partial
or total lack of sensation
(numbness), burning or pain that usually begins at the tips of the toes or
fingers and gradually spreads upward.
There are 4 types of diabetic neuropathy
- It is very dangerous if the patient does not aware to the injuries. About one-third of foot ulcers occur on the big toe.
- People with diabetes who are overweight, smokers, autoimmune factor, genetic susceptibility, mechanical injury to nerves and have a long history of diabetes more than 20 years tend to be at most risk. Patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus tend to have higher risk than those type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Screening
Distal
symmetric polyneuropathy (DPN) should be screened starting at diagnosis of type
2 diabetes and 5 years after the diagnosis for type 1 diabetes. A subsequent
screening should be done annually. Basically,
this disease can be diagnosed by the basis of symptoms, medical history, physical and neurologic examination.
The doctor will check the
patient’s:
- Blood pressure
- Heart rate
- Muscle strength, reflexes
- Sensitivity to position changes, vibration, temperature or light touch.
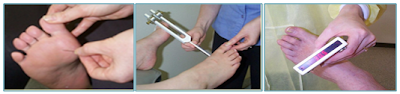
Test
Comprehensive foot exam
- A person who is having peripheral neuropathy requires frequent foot exams. The foot exam includes assessment of skin, muscles, bones, circulation and sensation of the feet. During this exam, the skin sensation and integrity, quantitative sensory testing (QST) and X-ray are done.
- The doctor will assess the protective sensation or feeling on patient’s feet by pricking your foot with a pin. If you can’t feel the pressure from a pinprick, then you are saying to at risk for developing foot sores due to lost protective sensation and this condition may not heal properly.
- Besides that, the doctor can also check temperature perception or use a tuning fork (more sensitive than touch pressure) to assess vibration perception.
Skin Prick Tuning fork Check temperature
Other
1) Nerve conduction studies and electromyographic exam
- Help in determining the type and extent of nerve damage.
- Is a nerve conduction studies to check the transmission of electrical current through a nerve.
- It measures how well and quickly the muscles and nerves conducting the electrical impulses.
- It records all electrical activity in the muscles.

2) Checking the variability of heart rate
- To evaluate the heart response to deep breathing and to the changes in blood pressure and posture.
3) Ultrasound
- Sound waves are used to produce an image of internal organs.
- · For example, an ultrasound of the bladder and other parts of the urinary tract can show us how those organs maintained a normal structure and to see whether the bladder is completely emptied after urination.
Treatment
There is no
specific treatment for patients with neuropathy. Normally, medications are
prescribed to reduce sign and symptoms. For example, antibiotics are commonly
used for patient with gastrointestinal problem; antidepressant and anticonvulsants
are used to relieve pain.
Foot Problems and Complications
Diabetes patient may develop different foot
problems. Serious complications may occur even there are only ordinary problem
related. Usually, that problem happens when nerve damage (neuropathy) occurred
and leads to loss of feeling in feet. Poor blood flow contributes to foot
problem and complications.
Risk factor for
foot disease:
·
Peripheral neuropathy
· Altered biomechanics ( changed mechanics of
function of a part of living body, such as of the heart or of locomotion of
muscle)
·
Evidence of increased pressure (callus,
erythema and bruising)
·
Reduced join mobility
·
Bony deformity
·
Marked nail pathology
·
Peripheral vascular disease
·
History of amputation and foot ulcer
Food care tips
GET STARTED NOW! Begin your foot care today.
Adapted from American Diabetic Association and American College of Foot
and Ankle Surgeon.
Other Complications
·
Erectile dysfunction
·
Sexual and urologic problem
Gastroparesis (A disorder of delayed stomach emptying results from
damaged vagus nerve.)
S Source:
National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse (NDIC), 2012.
http://diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
MedlinePlus, 2012. Diabetes and kidney disease http://www.nlm.nih.gov
ADA, 1995-2012. Kidney disease (Nephropathy) http://www.diabetes.org
Executive summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2012. Diabetes care, volume 35, Supplement 1, January 2012. care.diabetesjournals.org
National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse (NDIC), 2012.
http://diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
MedlinePlus, 2012. Diabetes and kidney disease http://www.nlm.nih.gov
ADA, 1995-2012. Kidney disease (Nephropathy) http://www.diabetes.org
Executive summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2012. Diabetes care, volume 35, Supplement 1, January 2012. care.diabetesjournals.org
































0 comments:
Post a Comment